Today's daf has a gynecological theme. The Talmud describes a dispute about when a woman is most fertile. One opinion is that "a woman only conceives close to her period" (אין אשה מתעברת אלה סמוך לווסתה), and a second opinion is that "a woman only conceives close to her immersion in a mikvah" (אין אשה מתעברת אלה סמוך לטבילתה). Today, we will figure out which of these competing medical theories is correct.
Medical students spend many hours learning the hormones whose rise and fall causes ovulation. But understanding the ovulation cycle is the key to understanding this passage in the Talmud, so let's spend a paragraph on...
Ovulation in women
There are two important hormones that regulate ovulation in a woman. One is called Follicle Stimulation Hormone, or FSH. This is produced in the pituitary gland deep in the brain and it acts on the ovaries to produce follicles, which are little groups of cells that may produce an egg. Under the action of FSH, the ovaries produce many follicles, but usually only one will go on to produce and release an egg. (If more than one follicle releases an egg, and both are fertilized, the result is non-identical twins.)
A sudden spike in FSH and another hormone called Luteinizing Hormone (LH) causes the winning follicle to release its egg, which floats down the Fallopian tube and into the uterus. If the egg meets a sperm cell, they unite and start down the pathway to producing a baby. But if no sperm cell is encountered, there is a drop in the level of two other critical hormones, progesterone and estrogen (also known as oestrogen for our British readers). This causes the lining of the uterus to slough off, and menstrual bleeding begins, until the whole cycle begins again.
Diagram from here.
Assuming a twenty-eight day cycle, the FSH-LH level peaks just before or around day fourteen, and these hormones trigger ovulation - the release of the egg from the ovaries - soon after.
“Scholars of the ancient world thought that menstruation represented an excess of blood from which the woman must periodically rid herself in order to cleanse her body from noxious substances. Only during the twentieth century has the scientific basis for the menstrual cycle and its hormonal relationships been clarified.”
Counting the Days to Mikveh
As outlined in the Torah (Leviticus 15:19), a menstruating woman is ritually unclean - Niddah - for seven days. After that she undergoes a ritual bathing in a mikveh, and she may resume physical and intimate contact with her husband. However the biblical seven day period was transformed in talmudic and later rabbinic tradition. The result was the addition of another (minimum) of five days to the length of time that a couple must abstain from physical intimacy. As a result, if we assume that day one of the onset of menstruation is the first day of the 28 day average menstrual cycle we discussed above, then the earliest day for a woman to immerse in the mikveh is on day twelve, or two days before ovulation is likely to occur.
The length of the menstrual cycle varies to a remarkable degree among different populations and in different age groups. In women age 19-41 in the US it varies from about 23 to 38 days (with a mean of 31 days.) In Danish women aged 20-35, however, the cycle is about 26-31 days, with a mean of 28 days. And each different cycle length will have its own ovulation day, and each varied ovulation day will affect the day on which conception is most likely.
Cycle length distributions for selected samples from various human populations. The numbers at the far left of each sample identify the corresponding sample and data. From Amy L. Harris & Virginia J. Vitzthum. Darwin's Legacy: An Evolutionary View of Women's Reproductive and Sexual Functioning, The Journal of Sex Research 2013. 50:3-4, 207-246.
The Timing of Sexual Intercourse and the Probability of Conception
The next issue in deciding which of the two opinions in today's page of Talmud might be correct is this: on which days around ovulation is a woman most fertile? This question was addressed in a study published in the esteemed New England Journal of Medicine in 1995. The authors followed 221 healthy woman who were trying to become pregnant (for a total of 625 menstrual cycles!!). The women kept records of when they had sexual intercourse, and their urine was tested for hormone metabolites to estimate the day of ovulation. The study found that "conception occurred only when intercourse took place during a six-day period that ended on the estimated day of ovulation." The authors note that couples who abstain from sexual intercourse until they have evidence of ovulation may miss the opportunity for conception.
Probability of Conception on Specific Days near the Day of Ovulation.
The bars represent probabilities calculated from data on 129 menstrual cycles in which sexual intercourse was recorded to have occurred on only a single day during the six-day interval ending on the day of ovulation (day 0). The solid line shows daily probabilities based on all 625 cycles, as estimated by a statistical model. From Wilcox A. et al. Timing of sexual intercourse in relation to ovulation. N Engl J Med 1995;333:1517-21.
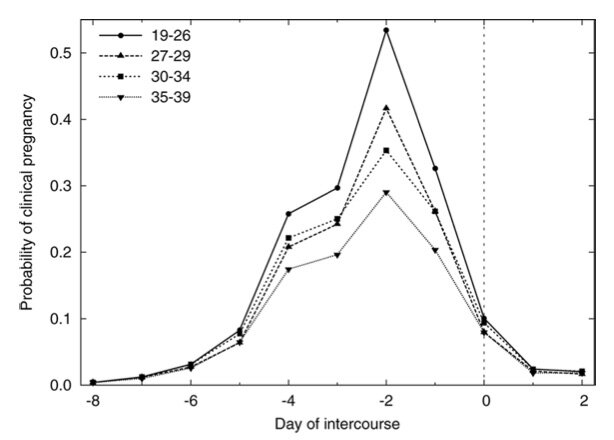
As you can see in the graph below, the day on which women are most likely to conceive is two to three days before ovulation. This is independent of their age.
Fertile window for four age groups. Probability of conception is highest for an act of intercourse occurring two days prior to ovulation. Redrawn from Dunson et al. (2002). Changes with age in the level and duration of fertility in the menstrual cycle. Human Reproduction, 17(5), 1399–1403, and cited in Amy L. Harris & Virginia J. Vitzthum. Darwin's Legacy: An Evolutionary View of Women's Reproductive and Sexual Functioning, The Journal of Sex Research 2013. 50:3-4, 207-246.
The chances of conception on a random day
In a review of the variability in ovarian function, Amy Harris and Virginia Vitzthum from Indiana University note that although it is the case that the fertile window is fairly narrow (about six days, ending within 24 hours after ovulation) “it does not follow that the fertile window occurs during a narrow range of days during the menstrual cycle. To the contrary, because the timing of ovulation during a cycle is quite variable, women have a 10% or greater probability of being in their fertile window on every day from cycle days 6 through 21, and more than 70% of women are in their fertile window before cycle day 10 or after cycle day 17.”
So they plotted the probability of conception on each cycle day and then calculated the mean probability of conception (i.e., clinical pregnancy following a single act of unprotected intercourse on a random day). What they found was that the average probability during cycle days 7-14 was 25% higher than that during cycle days 14-21. The average probability during the first two weeks of the cycle was 16% higher than that during the next two weeks. “Furthermore, in that subset of women who reported having irregular cycles, a not uncommon pattern, the average probability during cycle days 7-14 is less than half of that during cycle days 14 to 21.”
“Among healthy women trying to conceive, nearly all pregnancies can be attributed to intercourse during a six-day period ending on the day of ovulation. ”
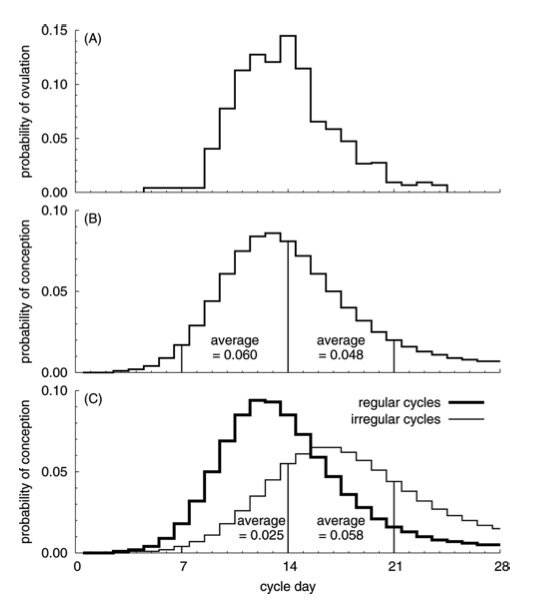
Panel A: The probability of ovulation by cycle day. Normal variation in the length of the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle: effect of chronological age.
Panel B: Daily probability of conception on each cycle day; mean probability of conception during cycle days 7 to 14= 6% and during cycle days 14 to 21 = 4.8%
Panel C: Daily probability of conception on each cycle day for women reporting regular cycles (thick line) and for those reporting irregular cycles (thin line); in latter sample, the average probability of conception during cycle days 7 to 14 is 2.5% and during cycle days 14 to 21 it is 5.8%.
Halakhic Infertility
Sometimes, a woman may be biologically fertile, but unable to conceive because of halakhic considerations. If a woman has a menstrual cycle that is shorter than the average 28 days (and about 20% of women have just that), or if a woman bleeds for more than 5 days (resulting in a longer Niddah time, in which the couple may not have intercourse,) then - and pay attention to this - then ovulation takes place during the Niddah time. And if that happens, as we noted above, then conception is all but impossible. This might be called halakhic infertility, and it is more common than you might have thought.
In a study of the prevalence of halakhic infertility in a population of ultra-orthodox Jews seeking help from a fertility clinic, a group from Hadassah Hospital in Jerusalem studied 45 infertile women. They found that precoital ovulation was prevalent in one-fifth (21%) of the patients. "Since not obeying the halachic code of conduct is non-negotiable, and in view of the void of halachic solutions, most couples (68%) seek medical advice and treatment." Fortunately such treatment is available: taking an an oral estrogen can delay ovulation to after the time of mikveh, and allow intercourse to take place at a time when conception is more likely.
“A fifth of infertile couples were diagnosed as suffering from infertility due to a religious rather than biological cause...This significant proportion of infertile couples who suffer from sociocultural infertility mandates special attention, primarily of the Rabbinate [sic] authorities.”
Back to the Daf - Which Opinion is Correct?
Let's now return to the question with which we opened; which of the following two opinions is correct?
A woman only conceives close to her period(אין אשה מתעברת אלה סמוך לווסתה).
A woman only conceives close to her immersion in a mikvah (אין אשה מתעברת אלה סמוך לטבילתה).
The first opinion is most certainly not supported by modern medicine. The second opinion is often likely to be true, but - and this is a BIG BUT - only for women for whom both the menstrual cycle is not short and menstrual bleeding is not long. For a sizable number of women, conception is no longer possible when they are ready to go to the mikveh.
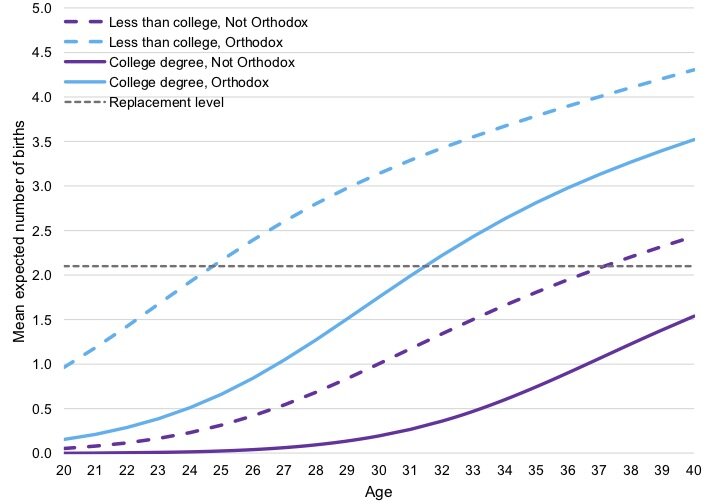
It is a remarkable fact (and one I have never seen addressed or even acknowledged) that orthodox Jewish practice has evolved to permit intercourse only in that part of the menstrual cycle which has a lower chance of conception. As a result, orthodox Jews have become in this respect, halachically subfertile. Fortunately that doesn’t seem to have made much of a dent in their rates of reproduction. “Being Orthodox” wrote Michelle Shain of the Center for Modern Jewish Studies at Brandeis, “increases the odds of having any births by a factor of 7.18 and, among women who have given birth, increases the expected number of births by a factor of 6.14.” Remarkably, this is in spite of, and not because of, the laws of ritual impurity that are a foundation of Jewish practice.
Mean expected number of births by age, education and Orthodoxy. From Michelle Shain, Understanding the Demographic Challenge: Education, Orthodoxy and the Fertility of American Jews. Contemporary Jewry 2019. 39: 273.
“Consultation with a Rabbinate [sic] authority was reported by 64% of women, but no halachic solution was provided to any of the applicants. ”